
September 19 - September 20
Waves Intro
Intro
Thursday
Friday
Pre-Test
What is a wave?
We will begin today with a brief introduction on waves. Then, you will have the opportunity to explore!
Mechanical Waves
We will begin today with a brief review of waves, then we will delve into types of mechanical waves!
Vocabulary Day
Longitudinal vs
Transverse Waves
Today we will be creating foldables for our binders reviewing key terms for our upcoming unit.
September 23 - September 27
Waves Intro
Essential Question: How is energy like a wave?
6.P.1.1 : Understand the properties of waves and the wavelike property of energy in earthquakes, light and sound waves.
Monday
Tuesday

Anatomy of a Wave
We will explore the parts of a wave
Labeling Waves
Today we will be reviewing the parts of longitudinal and transverse waves. We will start by drawing and labeling waves on our whiteboards. Then, we will complete review activities.

Wednesday - Friday
Stations

BASICS
EDPUZZLE
TRY IT
Check out the resource below. Use the resource as well as notes from your binder to complete the handout at your station.
Watch the Crash Course video on waves via EdPuzzle. (Go to google classroom to find the assignment).
Answer the questions to complete the video.
Practice what you have learned using the interactives.
Parts of a Wave
Types of Waves
Waves Practice
Virtual Lab
Real World
Checkpoint 1
Quarter 1
Ends
September 30 - October 4
Sound Waves
Essential Question: What is the nature of sound?
6.P.1.3 - Explain the relationship among the rate of vibration, the medium through which vibrations travel, sound and hearing.
Sound is a
longitudinal wave.
No School
What is Sound?
PITCH
What is pitch?
AMPLITUDE
What is amplitude?

Unit of Measure

AMPLITUDE
FREQUENCY
DECIBELS (dB)
HERTZ (Hz)
volume
pitch
THE EAR
How do we hear?
Topic Goals -
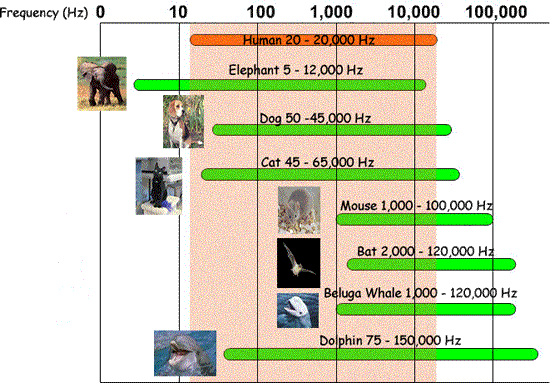
Something can be "heard" when sound waves from it enter the ear. Sound is a form of energy that is caused when vibrating materials produce waves that move through matter. The waves have different characteristics such as frequency and amplitude, which will determine the properties os sound such as pitch and loudness.
The form of the human ear can receive sound waves as vibrations and convert them to signals that are processed by the brain. Investigate how sound travels through different materials. Compare how sound travels through different states of matter. Investigate how vocal cords work to produce sound: structures of vocal cords, function of vocal cords and conditions that affect the sound vocal cords make. Investigate how the ear works: structures within the ear, functions of those structures, conditions that affect hearing.
LEVEL 4
October 7 - October 11
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Essential Question: What is the relationship between light and sight?
6.P.1.2 -Explain the relationship among visible light, the electromagnetic spectrum, and sight.
Monday/Tuesday
Finish stations from last week, turn in 6.P.1.3 work Tuesday.
Checkpoint 2
on Monday

Wednesday
Intro to EM Spectrum
Thursday
Exploring
EM Waves
Finish Early?
Real World Connections
You will explore a specific wave of the electromagnetic spectrum. (EMS)
You must research how their wave is used in a particular job field
In your binders, you must answer:
-
What EMS wave are you exploring?
-
What are the properties of the wave? (high frequency? Low frequency?)
-
What careers or jobs use your wave?
-
How does that wave work?
Friday
Checkpoint 3
October 14 - October 18
Light Waves
Essential Question: What is the relationship between light and sight?
6.P.1.2 -Explain the relationship among visible light, the electromagnetic spectrum, and sight.
6.P.3.2 -Explain the effects of electromagnetic waves on various materials to include absorption, scattering and change in temperature.



Something can be "seen" when light waves emitted or reflected by it enter the eye. Human eyes respond to only a narrow range of wavelengths of electromagnetic waves-visible light. Differences of wavelength within that range are perceived as differences of color. Light travels in
transverse waves. Light is a form of energy emitted by the Sun as well as light-producing objects on Earth. Light can be absorbed or reflected by objects depending upon the properties of the object and the type and angle of light when it hits the object. Some materials scatter light and others allow light rays to pass through, but refract the light by changing its speed.
Monday
Tuesday
Basics of Light
Colors
-Light Demo
Wednesday
Light Behaviors




Thursday
Lens Day!
-Lens Demo
Opaque
Translucent
Transparent

Friday
Checkpoint 4

Happy Track Out!
See you November 12
November 12 - November 15
How do we see?
Essential Question: What is the relationship between light and sight?
6.P.1.2 -Explain the relationship among visible light, the electromagnetic spectrum, and sight.
Alternatives to Dissection:
Dissection is one of many instructional methods that may be used in laboratory science courses. Students/parents/guardians may request alternatives to dissection from the teacher. Alternatives may include such materials as videos of dissections, virtual dissection simulations, models, charts, and diagrams.
Tuesday
Parts of the Eye
Light receptors within the eye transmit messages to the brain, which produces the familiar sensations of color. Newton observed that color is not inherent in objects. Rather, the surface of an object reflects some colors and absorbs all the others. We perceive only the reflected colors.
www.pantone.com/how-do-we-see-color
Wednesday - Part 2
Dissection Safety
Lab Write-Up
Wednesday (Part 1)
Dissection Procedure

Thursday
Dissection Day!
Friday
LAB WRITEUP
TO BE COMPLETED TODAY:
-Question (already typed)
-Purpose
-Background Research
- Start your procedure

November 18 - November 22
Lab Report
6.P.1
Understand the properties of waves and the wavelike property of energy in earthquakes, light and sound waves.
6.P.3
Understand characteristics of energy transfer and interactions of matter and energy.
Monday
Lab Write-Up
TO BE COMPLETED TODAY:
-Procedure
-Materials
-Observation

Tuesday
Lab Write-Up
TO BE COMPLETED TODAY:
-Conclusion (Paragraphs 1-3)
Wednesday
Lab Write-Up
Conclusion (Paragraphs 4-6)
FINAL DRAFT DUE TODAY
- proof read for errors
Thursday
UNIT REVIEW
End of Unit Minor
Friday
November 25 - November 26
Thanksgiving
Monday
END OF UNIT TEST
Tuesday

